Solar Installation
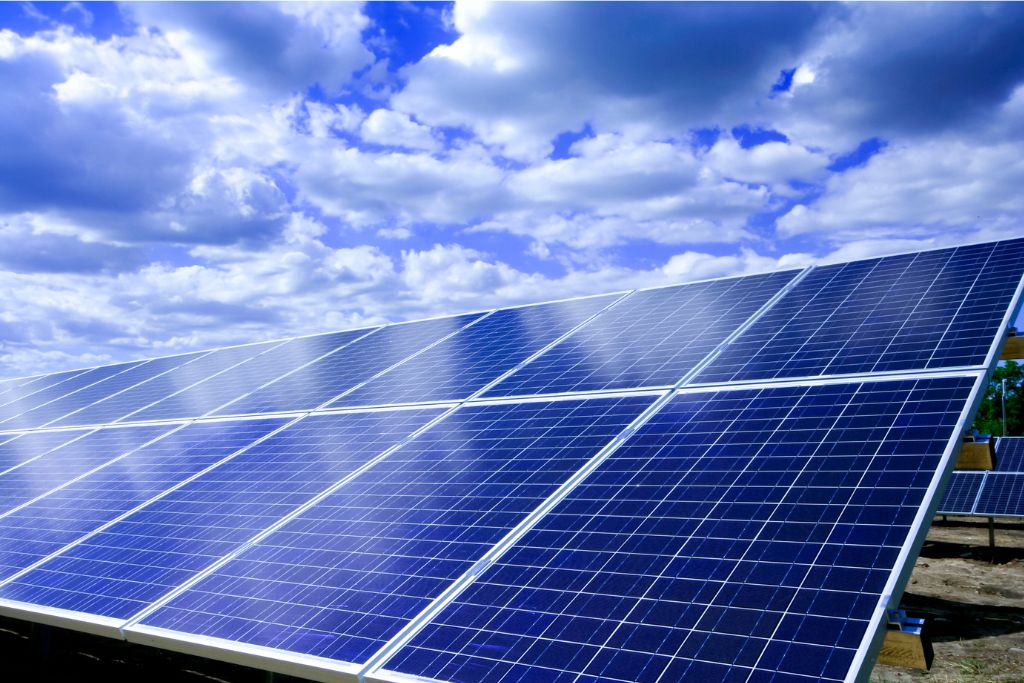

Solar Panels
Solar panels are devices that convert sunlight into electricity using photovoltaic (PV) cells. They are an eco-friendly energy solution for homes, businesses, and industries.
Types of Solar Panels:
- Monocrystalline Panels: High efficiency, sleek design, long lifespan.
- Polycrystalline Panels: Cost-effective, moderate efficiency.
- Thin-Film Panels: Lightweight, flexible, suitable for unique installations.
Popular Solar Panel Brands:
- LONGi Solar: Known for high-efficiency monocrystalline panels.
- JA Solar: Offers reliable and cost-effective solutions.
- Trina Solar: Focuses on performance and affordability.
- JinkoSolar: A leading global brand with high-quality products.
- Canadian Solar: Combines affordability with strong performance.
- LG Solar: Premium panels with advanced technology and design.
- SunPower: Industry leader in efficiency and durability.
- REC Solar: Known for high performance and environmental commitment.
- Q CELLS: Offers versatile solutions with excellent efficiency.
- First Solar: Specializes in thin-film solar technology.
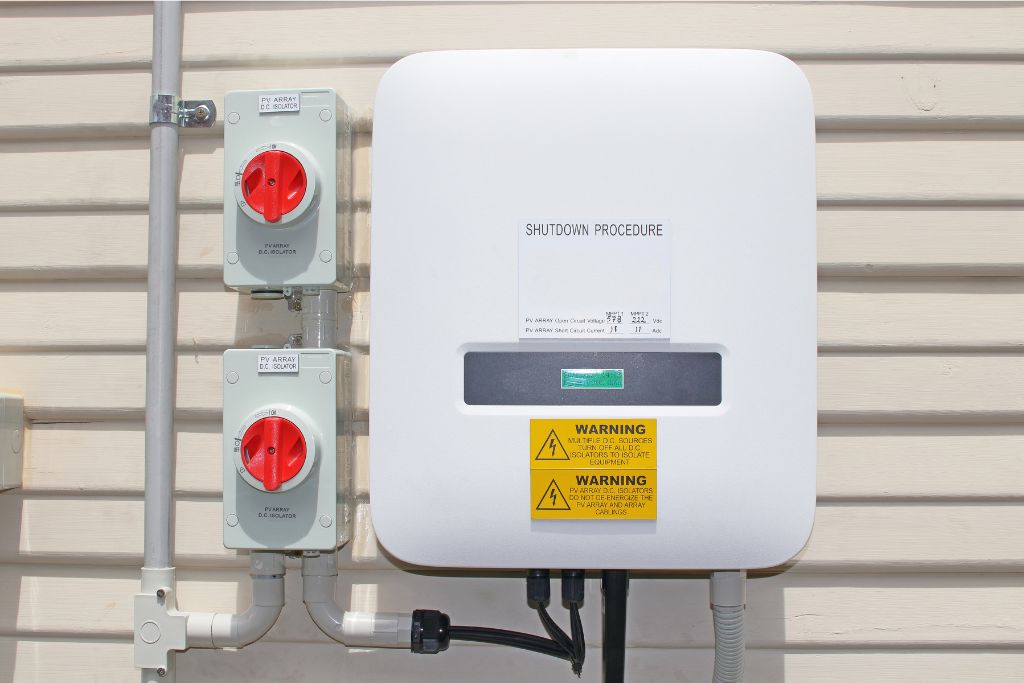

Inverters
Inverters are essential components of solar energy systems, converting the direct current (DC) electricity generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity, which is used by most appliances and fed into the grid.
Types of Solar Inverters:
String Inverters:
- Connect multiple panels in a series.
- Cost-effective and commonly used in residential and commercial setups.
- Efficiency may drop if one panel is shaded.
Microinverters:
- Installed on each solar panel for individual optimization.
- Ideal for areas with shading issues or complex panel layouts.
- Higher upfront cost but improved efficiency.
Power Optimizers:
- Work with string inverters to optimize panel output.
- Cost-effective alternative to microinverters.
Hybrid Inverters:
- Combine traditional inverter functionality with battery storage management.
- Allow for energy storage and off-grid operation.
Off-Grid Inverters:
- Designed for standalone systems without grid connection.
- Paired with battery systems for energy storage.
Popular Inverter Brands:
- SMA Solar Technology: High-quality string inverters with advanced features.
- Fronius: Known for reliability and innovative design.
- Huawei: Smart inverters with monitoring and efficiency optimization.
- SolarEdge: Specializes in power optimizers and monitoring systems.
- Enphase: Market leader in microinverters.
- Growatt: Affordable inverters with good performance.
- Victron Energy: Renowned for off-grid and hybrid inverter solutions.
- Delta Electronics: Durable and efficient inverters for various applications.
- GoodWe: High-quality inverters with integrated storage options.
- ABB/Hitachi Energy: Reliable and efficient inverters for large-scale projects.

Solar Batteries
Solar batteries store excess energy generated by solar panels for later use, allowing for greater energy independence and efficiency. They are especially useful in off-grid systems or during power outages.
Types of Solar Batteries:
Lead-Acid Batteries:
- Affordable and widely available.
- Shorter lifespan and lower depth of discharge (DoD).
Lithium-Ion Batteries:
- High energy density, long lifespan, and deep DoD.
- Lightweight and efficient.
Nickel-Cadmium (Ni-Cd) Batteries:
- Durable and capable of handling extreme temperatures.
- Expensive and less eco-friendly due to cadmium.
Flow Batteries:
- Long lifespan and scalable energy storage.
- Bulky and higher upfront cost.
Gel Batteries:
- A type of lead-acid battery with better performance and longevity.
- Maintenance-free and spill-proof.
Popular Battery Brands:
- LG Chem RESU: Compact and efficient lithium-ion storage solutions.
- BYD: Offers scalable and durable lithium-ion batteries.
- Sonnen: Premium residential batteries with smart energy management features.
- Panasonic: Reliable and efficient battery solutions for various applications.
- Enphase Encharge: Lithium-ion batteries designed for seamless use with Enphase systems.
- Blue Planet Energy: High-performance lithium-ion phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries.
- Varta: Known for reliable and long-lasting battery technology.
- Redflow: Specializes in flow batteries for large-scale applications.
- Duracell: Offers cost-effective and durable solar battery solutions.
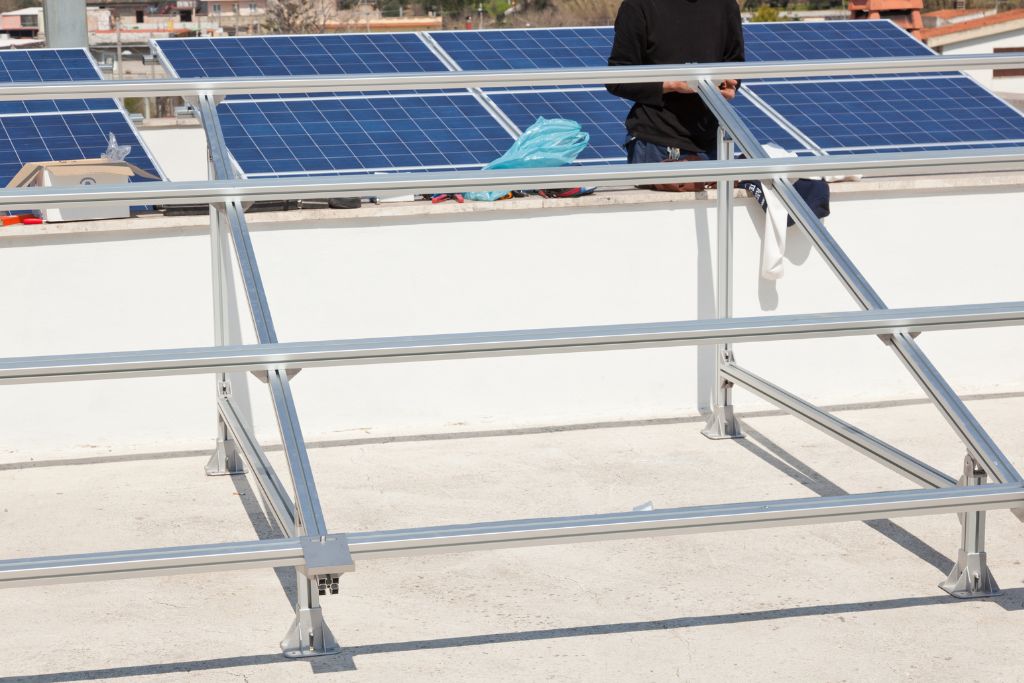

Solar Panel Structure
The solar panel structure refers to the framework or mounting system that supports solar panels and keeps them securely in place, whether they’re installed on rooftops, ground mounts, or solar farms. The structure plays an essential role in ensuring the durability and efficiency of the solar energy system by withstanding various environmental conditions.
Types of Solar Panel Structure Installations:
Rooftop Installations:
- Residential or commercial rooftops are often the most convenient and cost-effective places to install solar panels. The structure supports the panels while keeping them securely fixed to the roof.
- Types: Flat roofs or sloped roofs with appropriate brackets and mounts.
Ground-Mounted Installations:
- These structures are used when roof space is limited or not suitable. Panels are installed on frames on the ground, which can be customized to allow for optimal solar exposure.
Solar Farms:
- Large-scale solar installations where thousands of solar panels are mounted on specialized racks and structures across a vast area. These structures are designed for maximum efficiency and minimal maintenance.
Benefits of a Strong Solar Panel Structure:
- Enhanced Durability: Ensures the panels withstand environmental stress like wind, rain, snow, and extreme temperatures.
- Optimal Performance: Keeps panels at the best angle for maximum energy production.
- Safety: Provides stability and safety to prevent panels from shifting or falling, reducing risks from storms or natural disasters.
- Easy Maintenance: Allows for straightforward cleaning, inspection, and repairs when needed.
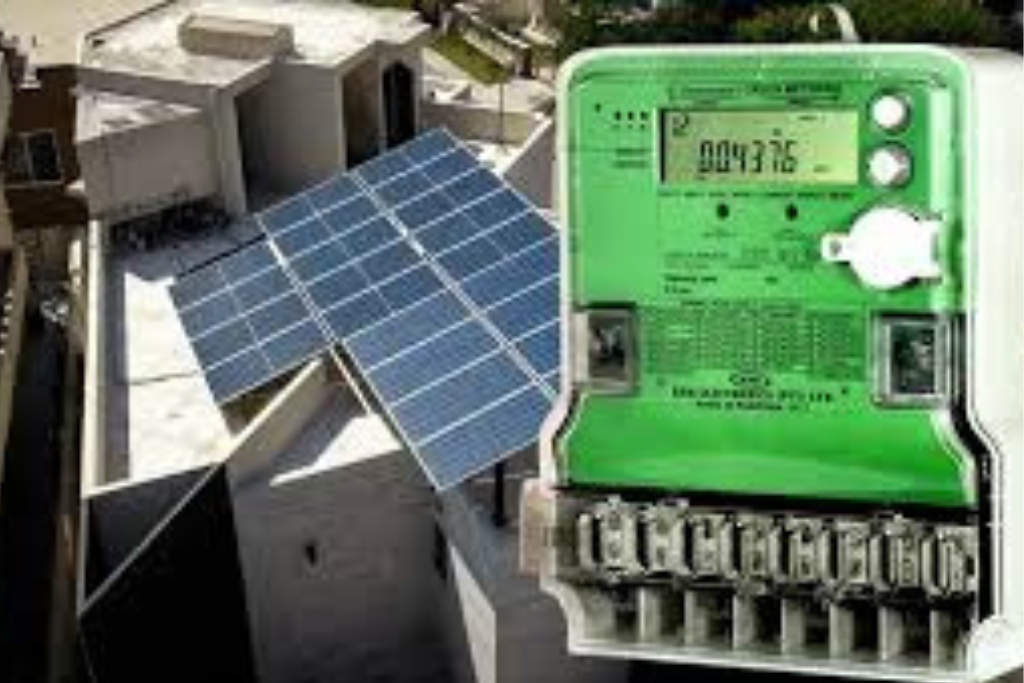

Net Metering
Net metering is a system that allows consumers to generate their own electricity using solar panels and feed excess electricity back into the grid. In Pakistan, net metering allows residential, commercial, and industrial solar energy users to reduce their electricity bills by getting credit for the power they contribute to the national grid.
How Does Net Metering Work?
- Solar Panel Generation: Solar panels on a property generate electricity, typically during daylight hours.
- Consumption: The electricity generated is first used to power the property’s appliances. Any excess power not consumed is sent back to the national grid.
- Metering: A bi-directional meter measures both the electricity consumed from the grid and the excess energy fed back into it.
- Credits: For the electricity sent back to the grid, the consumer receives credits (usually in kilowatt-hours), which offset future electricity consumption.
Benefits of Net Metering :
- Cost Savings: Solar panel owners can lower their electricity bills by generating their own power and getting credit for surplus energy sent to the grid.
- Promotion of Renewable Energy: Net metering encourages the use of clean and sustainable solar energy, contributing to environmental sustainability.
- Energy Independence: Helps reduce reliance on the national grid, providing a backup energy source in case of power outages.
- Revenue Generation: Consumers can earn credits or compensation from excess electricity, making solar energy more financially viable.
- Government Incentives: The Pakistani government offers various incentives and subsidies for solar energy adoption, including tax exemptions on equipment.
Solar Energy System Accessories
Solar energy systems consist of various components that work together to generate, store, and manage electricity. Accessories are essential parts of these systems to ensure optimal performance, safety, and efficiency. Here’s an overview of the key accessories used in solar energy systems.
Key Solar System Accessories
Solar Charge Controllers: Regulate power from solar panels to prevent overcharging of batteries (PWM or MPPT types).
Inverters: Convert DC electricity from panels to AC for home use or grid connection (String, Micro, Hybrid).
Battery Storage: Stores excess solar energy for later use (Lead-Acid, Lithium-Ion, Flow Batteries).
Mounting/Racking Systems: Secure solar panels on roofs or the ground, optimizing sunlight exposure.
Bi-Directional Meter: Measures both energy consumed and excess energy sent to the grid for net metering.
Disconnects & Fuses: Provide safety by disconnecting the system from the grid or batteries during maintenance.
Solar Cables & Wiring: Connect solar components, ensuring safe and efficient energy flow.
Surge Protectors: Safeguard the system from power surges caused by lightning or grid fluctuations.
Battery Management System (BMS): Monitors and manages the health of solar batteries, ensuring longevity.
Solar Panel Cleaning Tools: Brushes, waterless kits, and robots for keeping panels clean and efficient.
